The core applications of plantar pressure analysis in clinical medicine can be categorized into the following areas:
I. Diagnosis of foot diseases
Structural abnormality screening
Identifying flat feet (even pressure on the medial longitudinal arch) and high-arch feet (concentrated pressure on the forefoot and heel) through static pressure mapping
Dynamic analysis can quantify the center of pressure deviation trajectory in patients with inversion/valgus foot, assisting in the development of orthotic treatment plans
Diabetic foot management
Early warning of foot ulcer risk: localizing high pressure areas on the forefoot or heel (>25 N/cm² requires intervention)
Monitoring pressure redistribution during ulcer healing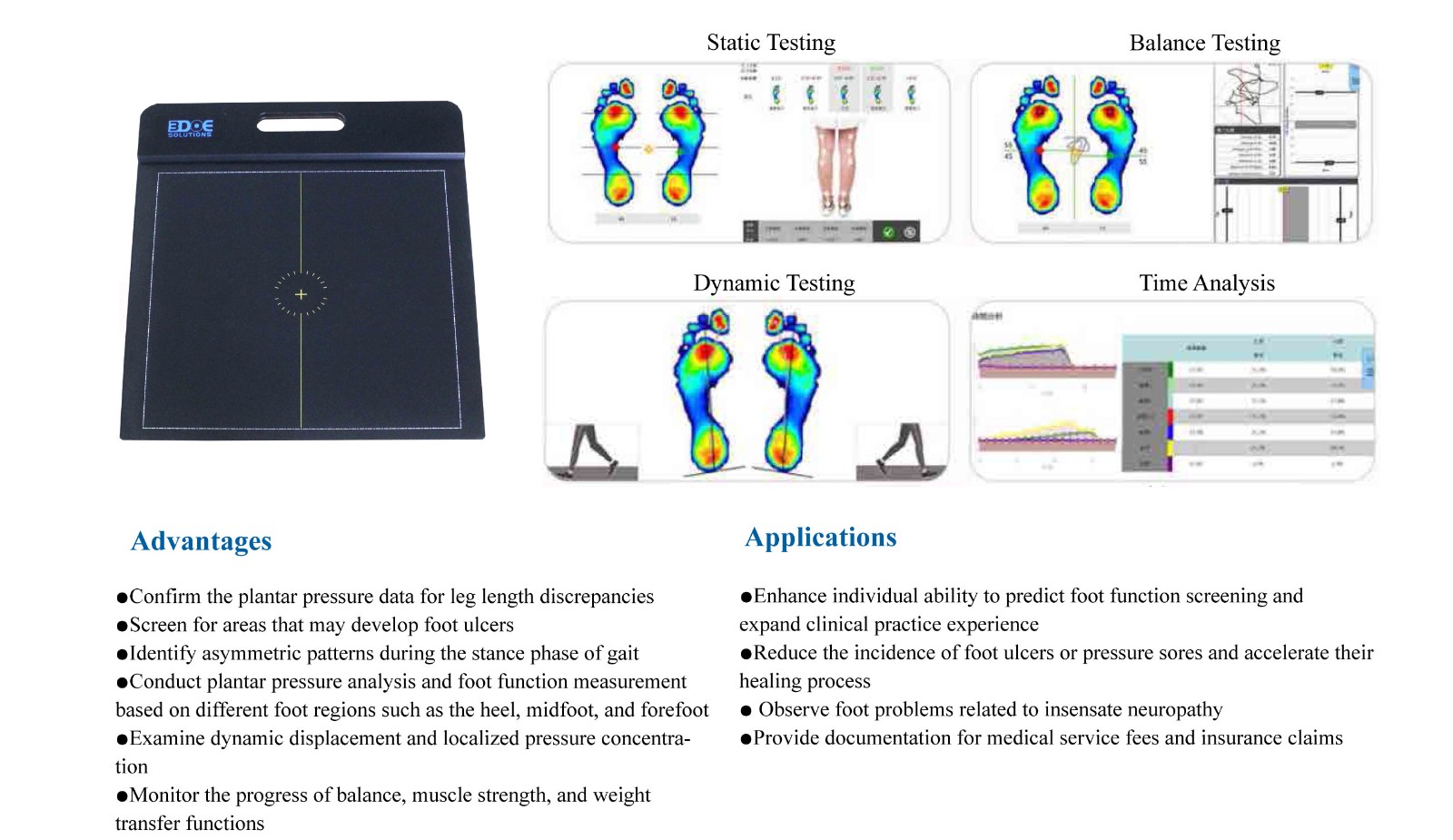
II. Neurorehabilitation assessment
Gait analysis after stroke
Assessing gait symmetry using the COP (center of pressure) trajectory and quantifying the pressure difference between the affected and unaffected sides (>15% indicates abnormality)
Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation
Detecting hip pressure distribution during sitting balance to prevent pressure ulcers
III. Sports Medicine Intervention
Sports Injury Prevention
Analyzing running strike patterns (e.g., excessive forefoot impact > 3 times body weight requires adjustment)
Postoperative Functional Recovery
Tracking changes in weight bearing after fracture or joint replacement surgery
IV. Child Development Monitoring
Tracking the arch formation process in children aged 3-12 years to detect flatfoot tendencies early (an arch index < 0.3 indicates abnormality)
Evaluating the effectiveness of orthotic insoles in improving gait in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
V. Elderly Health Management
Fall Risk Assessment: Detecting the center of mass swing ellipse using the Sway test (> 4 cm² indicates high risk)
Customized pressure-relieving insoles to relieve osteoarthritis pain

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-08-04
2025-08-04 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192