The foot pressure distribution system and the foot scanner can usually work together in fields such as sports medicine, rehabilitation treatment, gait analysis, and personalized equipment design. Although they have different measurement methods and data characteristics, when used together, they can provide users with more comprehensive and accurate foot analysis and health assessment. Here is how they collaborate and their advantages: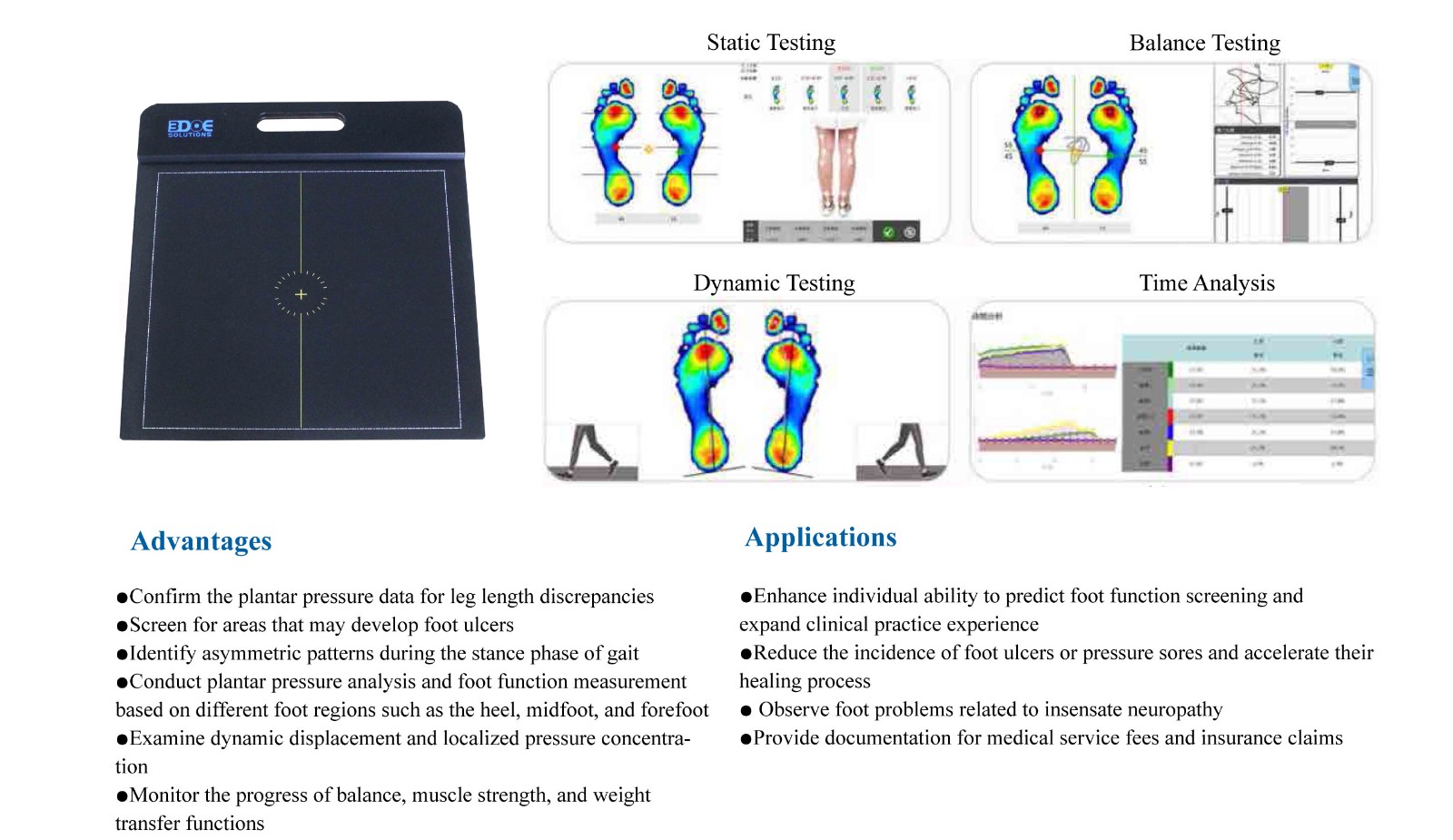
1. Complementary System Functions and Data Characteristics
Foot Pressure Distribution System:
Primarily measures the pressure distribution and changes in various areas of the foot during gait, walking, or running through a sensor array.
The focus of analysis is on dynamic force, gait parameters, center of pressure (COP) trajectories, etc., providing real-time foot pressure data during movement.
Foot Scanner:
The foot scanner typically uses optical imaging, laser scanning, or 3D scanning technology to scan the foot's shape, arch height, foot contours, and other static structural data.
It is mainly used to assess the static shape of the foot, such as arch form, foot width, and the relative position of the heel and toes.
2. Collaboration Method and Process
By combining the foot pressure distribution system and the foot scanner, more accurate personalized analysis and optimization can be achieved. The specific collaboration methods are as follows:
2.1 Initial Evaluation and Static Data Collection (Foot Scanner)
Static Foot Shape Scanning:
Arch height (normal/high arch/flat feet)
Foot width, heel shape, foot contours
Center of pressure (based on foot contact points)
First, use the foot scanner to scan the foot of the patient or athlete to obtain static structural data, such as:
These static data help us understand the basic structure of the foot and identify any structural issues (such as high or low arches, flat feet, etc.).
Providing Background for Pressure Distribution Analysis:
The foot structure data provided by the scanner will serve as important background information for subsequent foot pressure testing. For example, understanding the athlete or patient’s arch height and foot structure can help assess the potential impact on pressure distribution.
2.2 Dynamic Gait Analysis and Pressure Distribution Collection (Foot Pressure Distribution System)
Dynamic Gait Pressure Testing:
After understanding the foot's static structure, use the foot pressure distribution system for gait analysis. During walking or running, the sensor array captures the pressure changes of the foot with each landing, generating pressure distribution maps.
During this process, pressure data will reveal the pressure distribution across different areas of the foot, center of pressure (COP) trajectory, step frequency, step length, and other dynamic data.
Comparing and Analyzing Pressure Data with Static Data:
By combining static foot scanner data with dynamic pressure distribution data, a more comprehensive assessment of foot health can be made.
For example, for individuals with high arches, the pressure distribution system may find that they have greater pressure in the forefoot and heel areas during gait, which could lead to increased foot fatigue or injury.
For individuals with flat feet, the foot pressure distribution might show lower pressure in the arch area while walking, leading to poor load distribution on the ankles, knees, and even the spine.
2.3 Data Integration and Personalized Plan Formulation
Personalized Analysis and Recommendations:
Sports Performance Optimization: Based on foot structure (such as arch) and pressure distribution data, personalized sports recommendations can be provided, such as stride adjustment or running posture optimization.
Custom Insoles or Orthopedic Devices: Based on foot shape (scanner data) and pressure distribution (pressure system data), customized orthotic insoles or sports shoes can be made to meet the individual's needs.
Rehabilitation Tracking: For post-surgery or injured patients, by regularly using the foot scanner and pressure system, foot changes during the rehabilitation process can be tracked, and gait recovery can be evaluated, further adjusting the treatment plan.
Combining the results of both can create personalized sports, rehabilitation, or treatment plans for athletes, patients, or general users.
3. Specific Collaboration Application Examples
3.1 Athlete Gait Analysis
Objective: Optimize sports performance and prevent sports injuries.
Process:
Use the foot scanner to obtain static foot data of the athlete (such as arch height, foot shape).
Use the foot pressure distribution system to conduct dynamic gait analysis and assess pressure distribution, step frequency, step length, etc., during movement.
Combine static and dynamic data to analyze the athlete's uneven force or poor gait during running or walking.
Based on the analysis results, provide running posture improvement plans, adjust shoe designs, or even customize orthotic insoles.
3.2 Rehabilitation Patient Monitoring
Objective: Help patients recover and prevent reinjury.
Process:
Use the foot scanner to perform detailed shape scanning of the patient's foot to understand the foot structure.
Conduct gait analysis, especially for patients with foot injuries or post-surgery, by using the foot pressure analysis system to monitor their gait changes in real-time.
Combine static and dynamic data to detect gait issues in the rehabilitation process (such as excessive force on one side), and provide personalized rehabilitation training plans.
4. Advantages of Collaboration
Comprehensiveness: The combination of static data (foot shape) and dynamic data (gait pressure) makes the foot analysis more comprehensive, thereby more accurately identifying issues.
Personalized Customization: The combination of both systems can provide each user with a tailored sports, rehabilitation plan, or shoe design.
Accurate Assessment: The foot pressure distribution system provides detailed gait analysis, while the scanner offers detailed information about the foot structure, providing more precise data support for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention and Intervention: By combining dynamic and static data, potential gait issues can be detected earlier, allowing for timely prevention and intervention to avoid sports injuries or diseases.

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-09-22
2025-09-22 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192