Flat feet, high arches, foot valgus, foot varus, asymmetrical foot shapes, abnormal gait… these foot-related issues often affect walking comfort and lower-limb health.
Just as an optometry instrument and a vision chart have different testing focuses for the eyes, the 3D plantar scanner and the plantar pressure distribution system also different roles in foot assessment.
They often coexist, but they are not the same device. To obtain an accurate understanding of the foot condition, it is first necessary to clarify the difference between them. So, what differences actually exist between them? They can be understood as follows:
I. Different testing content: structure vs. loading
1. The 3D scanner mainly studies the structure of the foot
3D foot scanning mainly presents the external characteristics of the foot, including:
Arch morphology (high, medium, low)
Foot-shape outline (length–width ratio, instep height)
Toe alignment
Heel tilt direction
Structural differences between left and right feet
It is more like a “three-dimensional ID card” of the foot, providing static morphological information.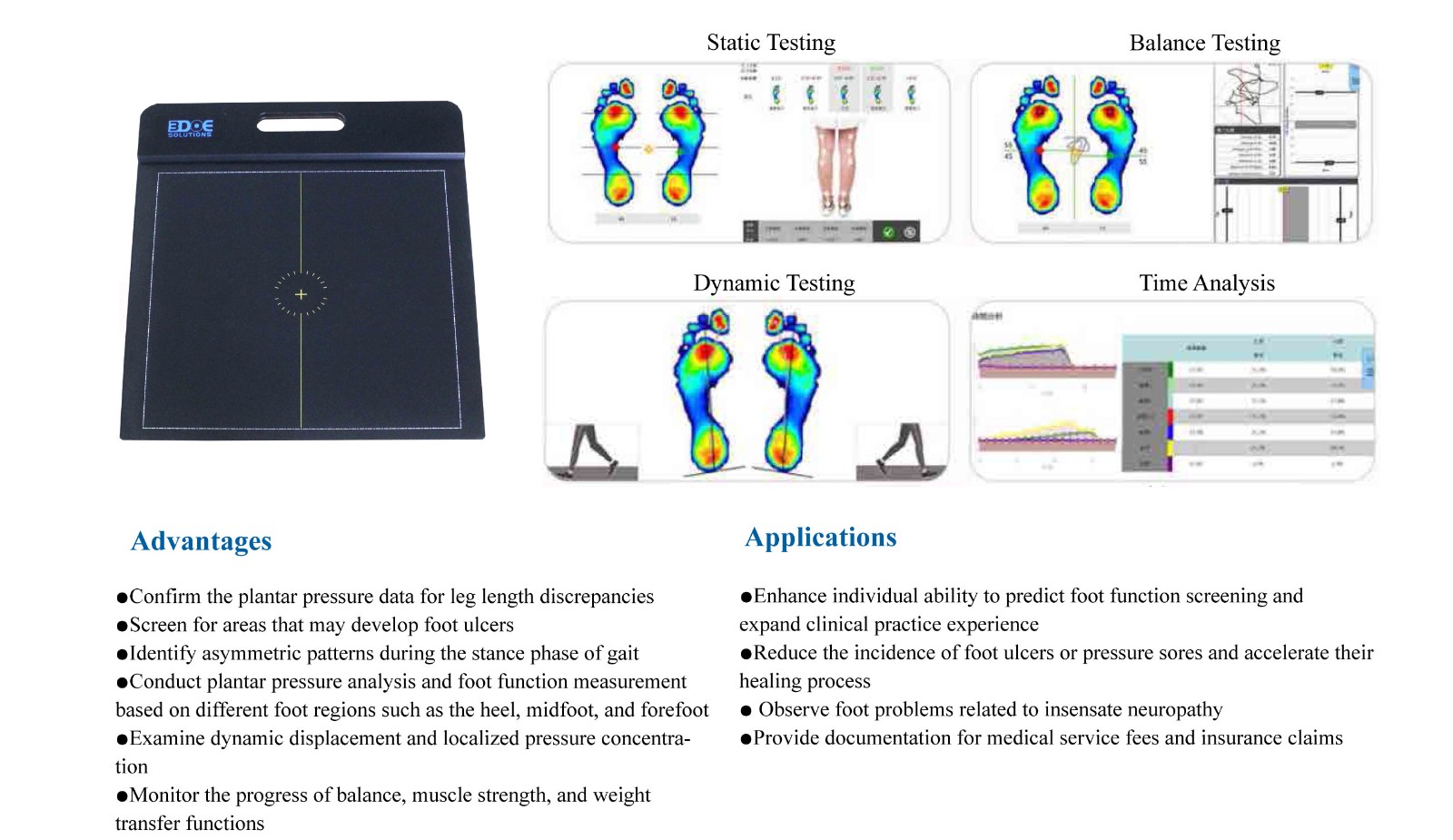
2. The pressure system mainly studies the loading condition of the foot
The plantar pressure distribution system is used to record foot forces during standing, walking, and acceleration, such as:
Which area bears more force
The order in which the foot touches the ground
Whether the pace is balanced
The movement path of the center of pressure (COP)
It displays the foot’s dynamic performance and “plantar force map.”
II. Different application purposes: examining morphology vs. examining function
1. Using a 3D scanner to analyze foot structure
By using morphological data, one can determine what “shape” the foot has:
Understanding foot-shape characteristics
Judging shoe size, instep height, and forefoot width
Analyzing the static condition of the arch
Making customized insoles or shoe lasts
More inclined toward “structural evaluation.”
2. Using the pressure system to evaluate foot function
Forces and gait are a form of functional performance, used to:
Determine whether walking posture is normal
Evaluate lower-limb force lines
Identify abnormal force points
Analyze whether movement has potential risk
More inclined toward “movement and functional evaluation.”
III. Different testing methods: static imaging vs. dynamic monitoring
1. 3D scanning is a type of static acquisition
As long as both feet stand still, the scanner can produce a complete foot model. The result is stable and does not rely on gait performance.
Suitable for all kinds of people, including children, the elderly, and those unable to walk.
2. Pressure distribution includes both dynamic and static states
It can detect both the pressure condition in static standing and the dynamic performance during walking.
Data acquisition requires movement, requiring the user to walk or run naturally.
IV. Different output results: 3D model vs. color pressure map
1. 3D scanning outputs an actual foot model
Usually presents:
3D images of arch height
Heel tilt angle
Toe shape and dorsal structure
Specific dimensional data for each part
The representation is intuitive, similar to a “3D printing file.”
2. The pressure system outputs force distribution data
Common outputs include:
Pressure strength distribution indicated by different colors
Gait curves and trajectory lines
Pressure–time distribution charts
Symmetry analysis of both feet
The reading resembles a “heat map” or “movement trajectory diagram.”
V. Different roles in orthotic and health management
1. The 3D scanner provides the basis for insole shape
It tells the technician:
What the insole width should be
How high the arch support should be
How deep the heel cup should be
What curvature the forefoot area requires
More inclined toward “structural fitting.”
2. The pressure system provides reference for functional insole design
It tells the technician:
Which area needs cushioning
Which area requires stronger support
Whether gait needs correction
Whether force lines need adjustment
More inclined toward “functional correction.”

 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192 2025-11-17
2025-11-17 Back to list
Back to list








 +86-0755-86131192
+86-0755-86131192